This lesson will cover two fundamental methods in processing sound: delay and filtering. These techniques are related as filtering is based on a mixing a delayed sound with itself. Like all techniques covered in this class, this is only an introduction, there are many more ideas that can be developed beyond the patches presented here. The patches for this lesson can be downloaded here: 03-filters&delay
delay
 Delay is a method of transmitting sound through a media so that it can be heard later. This media can be magnetic tape, digital memory, or even the air.
Delay is a method of transmitting sound through a media so that it can be heard later. This media can be magnetic tape, digital memory, or even the air.
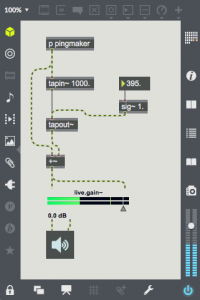
In Max this is done with two objects, tapin~ and tapout~. The audio memory is defined by tapin~, and tapout~ needs to be connected to tapin~ to have it use the tapin~ memory. The argument to tapin~ defines the maximum length of memory, in this patch that is 1000 ms. Both the argument and the input parameter to tapout~ is the delay time. In the case of this patch we are listening to the sound that entered the audio memory 395 ms ago. The tapout~ delay time will be limited to the length of audio memory defined. Any number of tapout~ objects can be connected to a single tapin~ object.
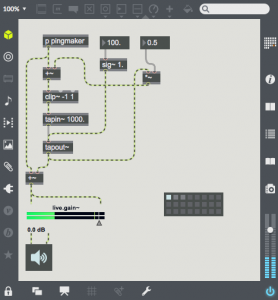 With many natural acoustic spaces (e.g. in a large room), the delayed sound re-enters the delay after it is heard, and the echo is repeated many times. This repeat can be easily added by sending some of the sound from tapout~ back into tapin~. In this patch, the output is multiplied by a feedback gain of 0.5 and added to the input signal before entering the delay line. This gain represents the gain reduction after each echo. If you select the first preset, you will here multiple decaying echoes. The second preset has much less gain reduction, and is an example of a rhythmic use of delay. The third preset shows the effect of having gain at or above 1.0. The signal soon clips and the delay memory soon fills with distortion. The clip~ object is essential to prevent the volume from getting out of control.
With many natural acoustic spaces (e.g. in a large room), the delayed sound re-enters the delay after it is heard, and the echo is repeated many times. This repeat can be easily added by sending some of the sound from tapout~ back into tapin~. In this patch, the output is multiplied by a feedback gain of 0.5 and added to the input signal before entering the delay line. This gain represents the gain reduction after each echo. If you select the first preset, you will here multiple decaying echoes. The second preset has much less gain reduction, and is an example of a rhythmic use of delay. The third preset shows the effect of having gain at or above 1.0. The signal soon clips and the delay memory soon fills with distortion. The clip~ object is essential to prevent the volume from getting out of control.
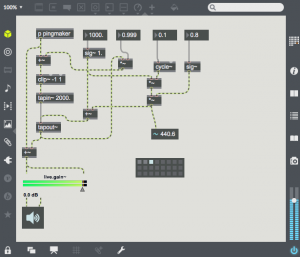 This next patch shows the simple addition of a sine oscillator as a modulation source for the delay time. When time is modulated, the period of any pitched material in the delay line is expanded and contracted. This will cause doppler pitch shifting effects. The 4 presets show various types of time modulation. The fourth example uses an audio frequency modulation oscillator. This will frequency modulate the contents of the delay memory. Flange, chorus and pitch shifting are all created using carefully tuned time modulation. Try to expand on this patch to create these effects. It will help to use sound sources other than the percussive “pingmaker” subpatch to demonstrate these effects.
This next patch shows the simple addition of a sine oscillator as a modulation source for the delay time. When time is modulated, the period of any pitched material in the delay line is expanded and contracted. This will cause doppler pitch shifting effects. The 4 presets show various types of time modulation. The fourth example uses an audio frequency modulation oscillator. This will frequency modulate the contents of the delay memory. Flange, chorus and pitch shifting are all created using carefully tuned time modulation. Try to expand on this patch to create these effects. It will help to use sound sources other than the percussive “pingmaker” subpatch to demonstrate these effects.
to be continued….
